21 Blockchain (Crypto) Myths. Know The Truth (Facts)!
*Get your crypto project/offer published on this blog and news sites. Email:contact@cryptoexponentials.com
Crypto space is full of opportunities, but it is essential to invest with care in this new market. My favorite blockchain myths & truths that help you better prepare to participate in crypto marketplace.
Myth 1: All crypto tokens are Ponzis
Truth: Many crypto tokens are Ponzis, some of them are definitely not. Here are five times investors got more than they bargained for from bad actors in the blockchain space. The hard challenge is to educate yourself to find ones that are not
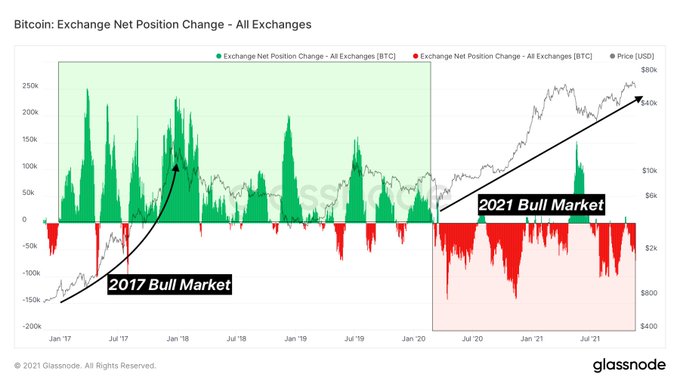
Myth 2: Buy the bloody DIP!
Truth: Not all dips comes with the same opportunity. Somes dips take “V” share recovery, few stays on “L” curve, and so on. You got the point. But the supply on exchanges continues to fall – a trend started in March, 2020. In this bull market really every dip looks like an opportunity..
Myth 3: Algo crypto coins can work, it’s a matter of finding a good design
Truth : Most (maybe all ?) algo coins will not survive brutal bear market as evidenced by BitUSD, NuBits and many others. Good stablecoin needs sound collateral
Myth 4: Enterprise businesses are not adopting blockchain
Truth. Fortune 500 companies across all sectors including banking, fintech, pharmaceutical, technology, agriculture, retail, and more are driving blockchain development.
Myth 5: Users don’t care about decentralization, they prefer fast txs and low fees
Truth : They will start to care if they are censored or rugged by unscrupulous centralised miners, either because they are dishonest or are forced by regulators
Myth 6: zkRollups cannot be rugged by their teams, because of the moon match
Truth: zkRollups can be rugged in a number of ways, most easily by including a backdoor in the circuit that is not detected by the larger community until it is too late
Myth 7: In zkRollups state growth is not a problem and they can scale almost infinetly
Truth: To achieve true censorship resistance users need to be able to independently reconstruct the state which will be a challenge if state growth is too fast for the average user to keep up with
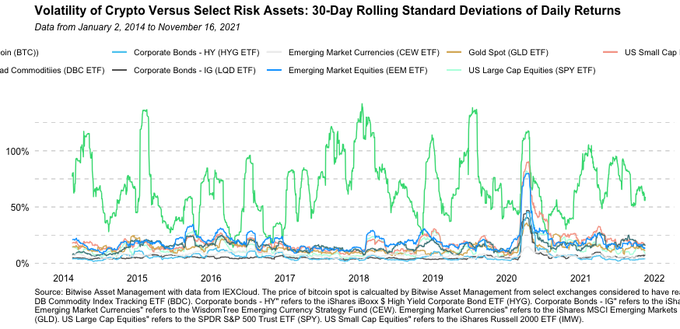
Myth 8: Bitcoin and cryptos are damn volatile
Truth: You got it! Bitcoin is a volatile asset. Most people who have spent time studying or investing in the asset already know this. Bitcoin is volatility is about 7x higher than the S&P500’s. Normalizing for that, a 12% move in BTC would be equivalent to a 1.7% move in the SPY. These are not uncommon: since 2014, the SPY has moved more than 1.7% or less than -1.7% in 141 out of 1978 sessions (7.1% of total).
Myth 9: Blockchains Are Costly and Inefficient
Truth. This depends on the structure of the blockchain, e.g. permissioned blockchains are usually more cost-effective and energy efficient compared to alternatives. Blockchains leverage a consensus mechanism known as proof of work (PoW), usually associated with permissionless networks mining cryptocurrency. However, permissioned networks and even some permissionless networks use consensus mechanisms other than PoW.
Myth 10: Users will prefer projects with sound tokenomics and super-star team that spent millions on security audits, formal verification and countless peer reviews of their protocols
Truth: Users prefer coins with dog meme
Myth 11: @sassal0x can single-handedly crush the market with one tweet given his superpowers and ungodly time zone in which he operates
Truth: This one may actually be true
Myth 12: ETH archive node is gigantic compared to Bitcoin archive node
Truth : ETH archive node allows you to query the state at any point from the past. It’s like asking Bitcoin node about UTXO set from a year ago. Comparison makes zero sense as the meaning of “archive” is different
Myth 13: There is no extra social layer in blockchains, consensus is programmed into the software and blockchains are truly immutable
Truth : Users can decide to change consensus rules, fork the blockchains, change history
Myth 14: Users will prefer immutable, code-is-law, blockchains over blockchain that changes former consensus rules
Truth : If programmed consensus rules seriously clash with what is understood to be the social consensus (the intent) users prefer a forked blockchain (ETH vs $ETC)
Myth 15: Above might be true for other blockchains but Bitcoin is immutable and consensus rules have never changed in the past
Truth : The consensus rules have been changed with Bitcoin in the past, they can be changed again
Myth 16: Ok, some rules in Bitcoin changed, but the 21.000.000 limit cannot be changed
Truth : We will seeQuote Tweet
Myth 17: All Data Put on a Blockchain Is Public
Truth: On a public blockchain, transactions are visible; however, identity is decoupled from the transactions. The parties in the transaction are represented by blockchain addresses (which look like a random string of characters). If the owners are careful, they will not be connected to any identifying information. Additionally, a piece of data, like a document, can be stored in a traditional secure cloud with a hash that would provide no value to other users as they would not be able to connect it to the document in the cloud. In a private/permissioned blockchain, access is restricted and managed by an administrator like any internal system.
Myth 17: Merge mining provides as much security as the “host” blockchain
Truth : Blockchains merge mined can be “destroyed” by host miners, it happened in the past, sometimes singlehandedly by individual actors
Myth 18: On-chain Oracles might be manipulated, but off-chain Oracles has never failed in the past, have huge Lindy effect and can secure multi-billion DeFi space
Truth : Off-chain Oracles failed in the past with disastrous effect blog.synthetix.ioSynthetix Response to Oracle IncidentOur response to today’s Oracle incident
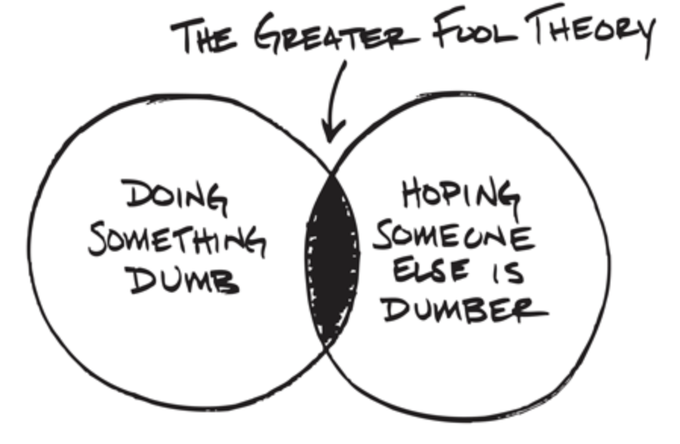
Myth 19: User will learn from past Ponzis and won’t participate in new ones
Truth : Users will try to recoup their losses from past Ponzis with the new ones hoping that this time they will find bigger fools than themselves
Myth 20: Blockchain Is Better than Traditional Databases
Truth. To some proponents, blockchain has never met a use case it didn’t like, but the individual use case will determine the best database. Blockchain has its pros and cons but may not be the best fit for a specific environment. CompTIA’s blockchain decision matrix provides some guidance on choosing the appropriate database type. It’s available at: s.comptia.org/BlockchainMatrix
Myth 21: Blockchain Is Immutable and Unhackable
Mostly True. Blockchains greatly increase the difficulty for a bad actor to access or change information, but they are not 100% unhackable. Transactions committed to a public/permissionless blockchain cannot be changed, however, private/permissioned blockchains do not inherently have that property because they lack a consensus algorithm and by the nature of being permissioned, an administrator can make changes. Public blockchains are vulnerable at the points where data is stored off-chain.
Now I leave you with a perspective. Comment on whether you think it’s a myth..
Myth??? “Ethereum will reduce its energy use by 99.95% with the switch to PoS”
1. When Ethereum switches to Proof of Stake, the energy use of the network will be reduced by about ~99.95%. One common reaction to this: “how can you be so sure?”
2. People are rightfully skeptical of claims about reduced energy use. When companies claim to be reducing emissions, the improvements are often marginal (and sometimes false). In that context, a reduction of 99.95% sounds too good to be true – more crypto snakeoil.
3. But Ethereum is different from things like cars, airplanes, and gaming consoles. You can’t power a car with money instead of energy. But you *can* secure a protocol with money instead of energy.
4. In “Proof of Work” cryptocurrencies, the high energy use is a proxy for a financial cost. If it is expensive to mine, then it is expensive to gain majority control of the network. In PoW, that expense comes in the form of energy
5. With the switch to “Proof of Stake”, we’re not just tweaking this system to make it more energy efficient. We’re completely substituting out the role of energy in the protocol, and directly using a financial cost – stake – instead.
6. From then on, the energy cost is just running client software – about 2.6 MWh per year (https://ethereum.org/en/nft/#fn-1) At that point, the US gaming industry will consume ~1,300 times as much energy as @ethereum (https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs40869-019-00084-2…)
Related Reading: Is Bitcoin Four Year Cycle Dead? “Uncover The Future of Bitcoin”
Sponsered
Start Earning Passive Cryptocurrency with Helium Hotspot Mining. Check It!
Earn FREE HNT Tokens Daily with Helium Hotspot Mining. Start Your CRYPTO Passive Income Now!