Supply Base Rationalization – Decison Sciences Approach
*Get your crypto project/offer published on this blog and news sites. Email:contact@cryptoexponentials.com
Within the area of strategic purchasing, the number of suppliers to maintain in a firm’s supply base is a critical component. Transactional purchasing performance is generally enhanced by larger numbers of suppliers that compete fiercely against each other for a share of business. Strategic purchasing, however, is enhanced by smaller numbers of suppliers that maintain long-term business relationships characterized by loyalty, openness, and trust. Yes, I’m talking about scientific way for supply base rationalization.
Supply Base Rationalization – Key Determinants:
Few of the key determinants of finding right number suppliers include,
Economies of scale: With a larger percentage of the business, firms have greater economies of scale to enhance their financial performance and provide the resource slack necessary to maintain the inter-firm collaboration and long-term investments needed to jointly succeed with their buying firm partner
Supplier performance diversity: While it is important for a firm to pursue a rationalization strategy that includes the best suppliers, it may also be incumbent on the firm to seek a diversity of performance capabilities within the reduced supply base. Ignoring this consideration could leave a firm undergoing supplier rationalization with a smaller but more redundant strategic supply base. This is more relevant in today’s environment of digital sourcing where large number discrete contracts with niche players is the visible phenomenon.
Product lifecycle considerations: Consumers that consistently purchase newly launched products are less price sensitive than are late adopters. These early adopters may also value speed to market and functionality more so than do the technology laggards. As these phases of the product life cycle attract different buying segments, strategic sourcing calls for different outcomes according to the different stages of the product life cycle. In the context of supply base rationalization, strategic sourcing organizes a reduced supply base structure thus still have to support the required diversity of firm objectives and life cycle considerations for those resource inputs deemed strategic to the firm
Supply base rationalization criteria:
The most common set of variables that many Sourcing organization aim to optimize while modelling supply base rationalization include, i) net-price, ii) quality, iii) delivery, iv) performance history, v) warranties and penalities, vi) facilities and capacity and vii) geographic location. So the objective function of supplier rationalization is to optimize the above relevant criteria.
A Practical Framework Considering Supplier Diversity Performance :
A reduced supply base enables management to focus time and resources on developing deeper supplier relationships with those firms remaining meeting the objectives as defined above. Provided that these suppliers have resources and capabilities that are aligned with the strategic objectives of the buying firm, the process of supply base rationalization can then be said to have critical strategic value to the firm. Hence supplier performance diversity plays a key role in this.
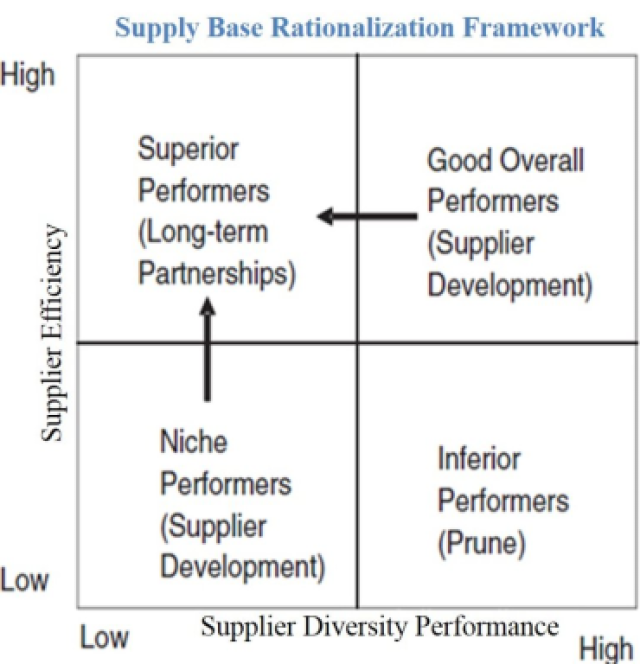
In the context of supply base rationalization, the careful and deliberate selection not only of high performing suppliers but also of suppliers that provide performance diversity across multiple dimensions is critical to structuring a supply base that supports the higher-level strategic objectives of the firm, especially when those objectives involve multi-dexterous capabilities. One such framework using Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) that operationalizes the process of simultaneously considering supplier performance and supplier performance diversity is presented above. This framework overlay what is supplier efficiency (Y-Axis) as per the success criteria defined and how suppliers differ in terms of performance diversity (X-Axis).Suppliers whose net efficiency is low and as well overall supplier diversity performance is low are NICHE Performers. Enterprises should focus on developing them to augment the capabilities of future. On the other side Suppliers who efficiency is high and supplier performance diversity is high are OVERALL GOOD performers. The long term objective of enterprises is have strategy to transform NICHE and GOOD suppliers to SUPERIOR performers offering higher efficiency and performance diversity to build next gen capabilities enabling business excellence.
For those firms engaged in supply base rationalization, whether or not to maintain diversity or redundancy across various performance dimensions is a strategic decision dependent on the objectives being pursued. I will further elaborate on decision sciences in the context of strategic sourcing in separate posts.
Appendix:
The following link provides a sneak peek into available supply base rationalization models and key tenants of the models. decision-model
Recommended Reading
Supplier Relationship Management: Unlocking the Hidden Value in Your Supply Base
Supplier Relationship Management enables organizations to secure vast value from their supply base by determining the suppliers that are important or hold potential and, based upon what makes them important or even strategic, putting in place interventions unique to each supplier to unlock real tangible benefits.





