New Age Healthcare Evolution Fueled By Digital reality
*Get your crypto project/offer published on this blog and news sites. Email:contact@cryptoexponentials.com
As Healthcare is shifting from being reactive to proactive, Digital is progressing that move a step further through intuitive aids that anticipate patient problems before they happen. Healthcare IT companies are attracting a lot of interest as a result of this. As per Analysts reports the digital healthcare industry has reached a new investment high in 2015. The past year saw nearly $5.8B invested, a two digit increase from the breakout year in 2014 (which itself saw more than double the funding over 2013). 2015 saw more than 1,000 entities that made an equity investment in at least 1 digital health company, up more than a 361% from the 234 that invested in digital health in 2010. The federal government is also on the rolls to spend up to $29 billion in incentives to encourage healthcare players to take advantage of digital investments. Does this enable new age healthcare evolution fueled by digital reality?
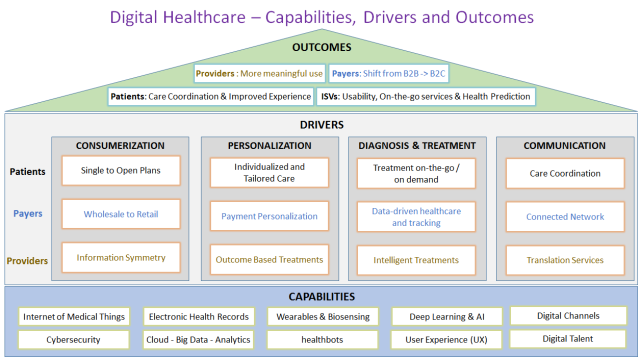
I) OUTCOMES:
Digital is contributing to enhance the outcomes of entire value chain of Healthcare touching all players in the ecosystem.
- Providers: Achieving “meaningful use”, which is the use of certified Electronic Health Records (EHR) technology to achieve health and efficiency goals.
- Payers: Enable payers to shift from B2B to B2C model of business for new consumer market that survive and thrive in this new reality
- Patients: Transforming healthcare delivery with promising care coordination and improved patient experience
- ISVs: Meeting healthcare organizations demand of better quality modules and features to allow enhanced usability, access to data in the cloud and on the go, and the liberty to analyze data for predicting patients’ future health
II) DRIVERS:
Just how is digital technology enabling healthcare evolution? Here are few drivers helping to achieving the above healthcare outcomes.
- CONSUMERIZATION: Healthcare is transforming from wholesale to retail. The patient or consumer, now expects the same experience in healthcare like in all other parts of their “consumer life.” This is a radical change is driving Patients take advantage of connected technologies, social tools, and information resources in more active role in their own health, and it extends further into the payer market. Consumers are no longer limited to the single plan offered by their employer – they have more options than ever on the open insurance market. To compete in this new marketplace, payers and providers need to rethink their offerings to give tailored experience to patients considering to provide plans that include performance incentives, transparency, and flexibility. The consumerization in Healthcare defines the problem statement for the Technology. Technology should enable industry collaboration and pricing transparency, increase hospitals use of business intelligence tools to derive patterns and consumer trends, solve information asymmetry between the medical professional and the patient and help overcoming the dichotomy between consumer and payer
- PERSONALIZATION: Healthcare industry has historically treated patients en masse. But the move from the group to the individual is inevitable now. Today’s healthcare consumers expect to be able to engage in a highly individualized, personalized manner, whether it’s in the services and treatments they receive, or the way they pay for that treatment afterwards. Technology should lead the personalization in Healthcare by building consumer centric CRM solution driving loyalty and providing personalized care is a key factor for sustaining long term growth for a healthcare organization. As well deploying advanced analytics will enable us to better understand which treatments deliver the best outcomes and to tailor treatment, messages, and services, as well as provide early alerts. And an increased emphasis from payers on branding themselves and sharing personalized, engaging content will help to differentiate them and build loyal relationships with consumers who have more choice than ever.
- DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT: The belief among industry practitioners is that Technology will replace 80% of what doctors do. Data-driven healthcare won’t replace physicians entirely, but it will help those receptive to technology perform their jobs better. Lifecom showed in clinical trials that medical assistants using a diagnostic knowledge engine were 91% accurate without using labs, imaging, or exams. A MassGen study found that 25% of the time, a medical record for patients who wound up with ‘high risk diagnoses’ had ‘high information clinical findings’ before a physician finally made the diagnosis — in other words, there was a significant delay that might have been avoided had a clinical decision support system been used to parse the notes! New technologies will make the receptive doctors better at their jobs – quicker, more accurate, and more fact-based. There is a tremendous opportunity in the influx of data that has never before been available. Once we have a large enough dataset, and an addressable database of research studies, we’ll be able to identify patterns and physiological interactions in ways that weren’t possible before. Another development worth mentioning is IBM invention of the computer “Dr. Watson.” the supercomputer to help physicians make better diagnoses and recommend treatments. Doctors could potentially rely on Watson to keep track of patient history, stay up-to-date on medical research and analyze treatment options.
- COMMUNICATION: Enabling doctor’s effective and easy communication with patients for improvising care coordination is another pertinent role of technology in Healthcare. One example to provide a perspective here is, Science Applications International Corporation (SAIC) development of Omnifluent Health, a translation program for doctors and others in the medical field. The suite of products includes a mobile app that lets doctors speak into the app — asking, for example, if a patient is allergic to penicillin — and translate the message instantly into another language. Given that there are 47 million U.S. residents who don’t speak English fluently, the program could be a boon for doctors who would otherwise need to rely on translators and medical assistants to communicate with their patients.
III) CAPABILITIES:
Building healthcare digital capability backbone encompassing all players of value chain – payers, providers and ISVs is critical in adopting to digital reality and realizing the true benefits. The key capabilities and their high-level usage patterns is discussed below.
- Internet of Medical Things (IoMT): IoMT is enabling remote patient monitoring of consumers with chronic or long-term conditions, tracking patient medication orders and the location of patients admitted to hospitals, and patients’ wearable devices, which can send information to caregivers. Telemedicine which is gaining momentum also use IoMT devices to remotely monitor patients at their homes.
- Electronic Health Records (HER): EHR is a digital version of a patient’s paper chart. EHRs are real-time, patient-centered records that make information available instantly and securely to authorized users. While an EHR does contain the medical and treatment histories of patients, an EHR system should be built to go beyond standard clinical data collected in a provider’s office and can be inclusive of a broader view of a patient’s care
- Cloud – Big Data – Analytics: For healthcare industry, the cloud seems a natural fit. From EHRs to data storage to software as a service (SaaS) capabilities, cloud-based products offer lower costs, greater capacity for scalability, dedicated service and support, and near-continuous uptime. But huge volumes of clinical data added to EHRs at every moment cannot be quickly and thoroughly translated into concrete, timely clinical decision support (CDS) information due to the limited computing resources of most healthcare organizations. Cloud-based analytics-as-a-service tools alleviate those pressure points and provide real-time CDS capabilities that will improve the quality of patient care by “combining the on-demand aspects of cloud computing with the democratization of information enabled by big data analytics.”
- Wearables & Bio-sensing: A growing number of mobile apps and gadgets aim to help people stay active, sleep well and eat healthy. Among them are Fitbit, a pedometer that tracks daily sleep and activity and uses social networking and gaming to motivate its users. Lark is a silent alarm clock and sleep monitor that tracks and analyzes a person’s quality of sleep over time, offering suggestions to help the person get better rest. And there are dozens of calorie-counting, food-monitoring and menu-tracking apps to aid the diet-conscious.
- healthbots: There is a growing experimentation to using robots as health aids for the elderly. People are opening up to the idea that robots and drones can be used as a force in healthcare. As aging population grows, so too will use of robotic health aids or ‘healthbots’.
- Deep Learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI finds purpose in healthcare. IBM’s Watson made a splash in 2015, and catalyzed the concept of AI in healthcare. These innovations are transitioning out of the lab and into the spotlight
- User Experience (UX): UX focus has acted as an important opening salvo in the integration of user-centered design principles into the healthcare industry processes, products, and workflows.
- Digital Channels: Omni channel digital capabilities are making healthcare more accessible, cost-effective, and engaged. Omni-channel healthcare opportunities empower people to seek care from anywhere and at any time, from their channel of choice (smartphone, tablet, computer, in-person). Importantly, it has the potential to improve overall health outcomes by minimizing a few key constraints that prevent people from receiving proper care — time, money, and a lack of engagement or knowledge
In summary, the future of healthcare is bright and exciting. Enormous strides have been made to move to a more personalized, meaningful model of care. New digital technologies and analytics are changing the way healthcare is delivered, and it’s important that healthcare players keep up this momentum to meet the needs of today’s patients.
Recommended Reading
The Infinite Retina: Spatial Computing, Augmented Reality, and how a collision of new technologies are bringing about the next tech revolution
A compelling and insightful look at the future of Spatial Computing, and how this cutting-edge technology is changing the way we do business across seven primary industries, and what it means for humanity as a whole.
Discover how Spatial Computing is changing the face of technology. Get a roadmap for the disruptions caused by Spatial Computing and how it will affect seven major industries. Gain insights about the past, present, and future of technology from the world’s leading experts and innovators






